ABOUT ANDERSON-COTTONWOOD
IRRIGATION DISTRICT
Anderson-Cottonwood Irrigation District in Anderson, California, holds senior pre-1914 appropriative water rights on the Sacramento River and is a Sacramento River Settlement Contractor.
ACID’s 32,000-acre service area begins just south of Redding and straddles Shasta and Tehama counties, on either side of the Sacramento River. The area is distinguished by its small-town rural charm, 300 days a year of sunshine, and vast outdoor recreational opportunities in the nearby mountains and on lakes and waterways.
ACID’s 800 customers primarily irrigate about 7,000 acres of pasture for hay and livestock.

water system
ACID diverts water from the Sacramento River using a seasonal dam on the river in Redding. The District also operates a pump station on the river about 4 miles downstream to supply a lateral canal. ACID’s distribution system includes approximately 35 miles of Main Canal, about 98 percent of which is unlined. The Main Canal flows through six inverted siphons to cross streams, such as Clear Creek, and three flume sections across smaller streams and lowland areas. When flow exceeds the canal capacity, District water overflows into several wasteways along the canal route.
Sacramento River Settlement Contract
The District is the fourth largest (in terms of water supply) of more than 100 Sacramento River Settlement Contractors. The Contractors divert water from the river under an agreement with the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation that was critical to development and operation of the Central Valley Project. The SRSCs work with federal and state agencies to manage water resources in the Sacramento Valley for multiple beneficial purposes that include water for cities, rural communities, farms, fish and wildlife and their habitats. ACID and other SRSCs fund numerous projects to protect resources such as watershed restoration and construction of fish passages.
The District is led by a five-member Board of Directors that continually seeks ways to improve service and viability through strong leadership, communication, system improvements and capital replacement projects.
history
Construction of ACID’s Main Canal began near Redding in 1914 and was completed in 1917.
The following year, the District’s 1,249-foot-long concrete flume, known as the aqueduct, was built to carry water across Anderson Gulch in Anderson south to the Bowman Road area of Cottonwood in Tehama County. The flume, which stands 20 feet above the ground, is composed of an 8-by-5-foot concrete box supported by open spandrel arch spans. The structure still stands and functions today and is designated as a point of historical interest.
Instrumental in the formation of Anderson-Cottonwood Irrigation District was Francis C. Carr (1875-1944), a justice of the peace, water rights attorney and State Water Commissioner. He also advocated for the construction of Shasta Dam and Whiskeytown Lake, about 8 miles west of Redding.
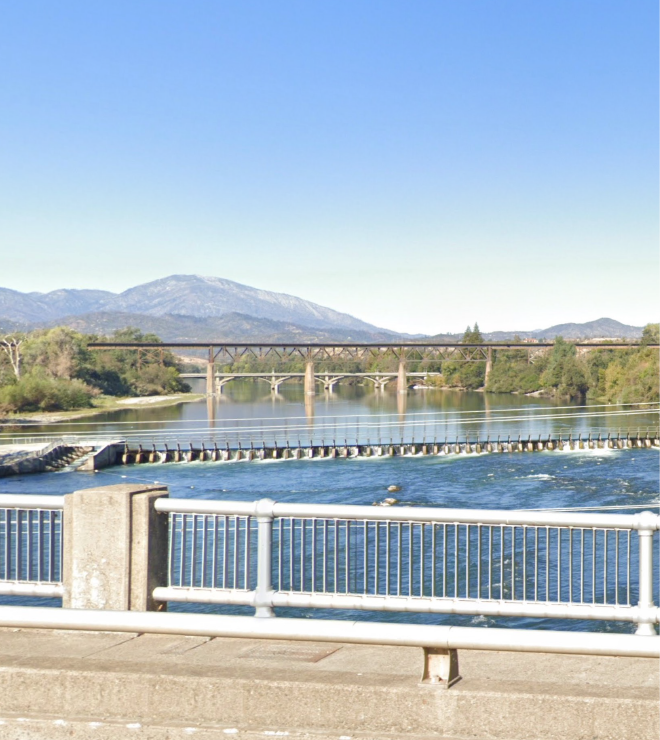


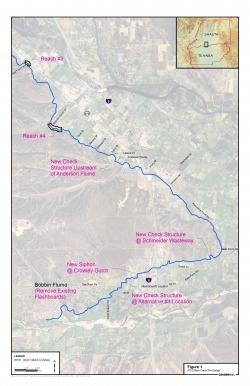 Anderson-Cottonwood Irrigation District (ACID or District) diverts water from the Sacramento River in Redding, California, primarily from a gravity diversion in the river at the seasonal ACID Diversion Dam in Redding. In addition, the District operates a pump station on the river approximately 4 miles downstream to supply a lateral canal. ACID’s distribution system includes approximately 35 miles of Main Canal, about 98 percent of which is unlined. The Main Canal flows through six inverted siphons to cross streams, such as Clear Creek, and three flume sections across smaller streams and lowland areas. When flow exceeds the canal capacity, District water overflows into several wasteways along the canal route (see Figure 2-1; figures are located at the end of each section in which they are first referenced).
Anderson-Cottonwood Irrigation District (ACID or District) diverts water from the Sacramento River in Redding, California, primarily from a gravity diversion in the river at the seasonal ACID Diversion Dam in Redding. In addition, the District operates a pump station on the river approximately 4 miles downstream to supply a lateral canal. ACID’s distribution system includes approximately 35 miles of Main Canal, about 98 percent of which is unlined. The Main Canal flows through six inverted siphons to cross streams, such as Clear Creek, and three flume sections across smaller streams and lowland areas. When flow exceeds the canal capacity, District water overflows into several wasteways along the canal route (see Figure 2-1; figures are located at the end of each section in which they are first referenced).